Introduction
Smart factories are transforming the world of manufacturing. With the integration of cutting-edge technologies, these factories are becoming more agile, efficient, and intelligent. This blog will explore the emerging trends and technologies that are shaping the future of smart factories, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and digital twins. We will also discuss how these advancements are improving productivity, quality, and sustainability.
1. What Are Smart Factories?
A smart factory is a highly digitalized and connected environment where machines, systems, and humans work together seamlessly. These factories use data and automation to optimize production processes. Thanks to Industry 4.0, the fourth industrial revolution, smart factories are becoming the new standard in manufacturing.
Key elements include:
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Cloud Computing
- Robotics and Automation
These technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved decision-making.
2. Augmented Reality (AR) in Smart Factories
AR enhances the real world with digital information. In smart factories, AR is being used to train workers, guide assembly processes, and improve maintenance.
Benefits of AR:
- Reduced training time
- Fewer human errors
- Better maintenance accuracy
For example, a technician wearing AR glasses can see instructions overlaid directly onto a machine. This not only speeds up the process but also ensures better quality.
3. Virtual Reality (VR) for Training and Simulation
VR creates immersive environments for training, planning, and troubleshooting. In a smart factory, VR is especially useful for onboarding new employees or testing workflows before actual implementation.
Advantages of VR:
- Safe training environments
- Improved employee skills
- Reduced operational risks
Imagine a worker learning to operate a new machine using VR. They can practice as much as needed without any real-world consequences.
4. Digital Twins: The Mirror of Manufacturing
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical object, process, or system. In smart factories, digital twins help monitor and simulate operations in real time.
Digital Twin Benefits:
- Real-time monitoring
- Predictive analytics
- Better product design
By simulating various production scenarios, factories can optimize processes and reduce waste.
5. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML are powering predictive maintenance, quality control, and smart decision-making. These tools analyze data from sensors and systems to detect patterns, predict failures, and suggest improvements.
Key Contributions:
- Improved efficiency
- Better resource utilization
- Enhanced product quality
Shorter maintenance downtimes and fewer production defects are just some of the visible benefits.
6. The Role of IoT in Smart Manufacturing
IoT connects machines, tools, and systems to gather real-time data. This connectivity enables faster responses to changes and better inventory management.
IoT Use Cases:
- Real-time tracking
- Smart supply chains
- Energy management
For instance, sensors can alert managers about equipment issues before they cause downtime.
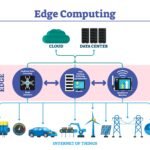
7. Cloud Computing and Edge Devices
Cloud computing enables scalable storage and powerful analytics. Combined with edge computing, data can be processed locally at the device level for faster responses.
Benefits:
- Scalable infrastructure
- Fast data processing
- Enhanced security
This setup supports faster decision-making and smooth data flows.
8. Cybersecurity in Smart Factories
With increased connectivity comes greater cybersecurity risk. Smart factories must secure their networks, devices, and data.
Key Measures:
- Multi-layer security
- Regular audits
- Employee training
Cybersecurity should not be an afterthought. Instead, it must be a core part of the smart factory design.
9. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Smart factories contribute to a greener planet by using energy-efficient systems and reducing waste.
Sustainable Practices:
- Smart lighting and HVAC
- Recycling and reusing materials
- Monitoring energy usage
Green factories not only protect the environment but also save costs.
10. Future Outlook and Innovations
The future of smart factories is exciting. Innovations like quantum computing, 5G, and autonomous robots will continue to reshape the landscape.
Predictions:
- More autonomous decision-making
- Personalized product manufacturing
- Greater collaboration between humans and machines
As these trends evolve, staying updated will be crucial for businesses aiming to stay competitive.
Conclusion
Smart factories are not just a vision—they are happening now. Technologies like AR, VR, and digital twins are paving the way for more efficient, safer, and sustainable manufacturing environments. By embracing these innovations, companies can improve productivity, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition.
Gourav Maheshwari
Compiled Successfully Software Solution
📧 CompiledSucessfully@gmail.com
📞 +91 92209 22267
https://compiledsuccessfully.in





Leave a Reply